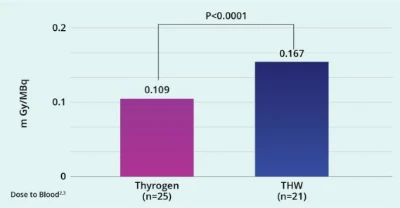
Thyrogen (rhTSH) decreased the mean absorbed dose to the blood by 35% thus reducing undesired radiation dose to the remainder of the body.2
- Thyrogen results in RAI uptake comparable to thyroid hormone withdrawal (THW), with 41% greater effective half-life than THW in thyroid remnant tissue (67.6 with rhTSH vs 48 hours with THW).
Study Overview
- 63 patients were randomized after thyroidectomy to either THW (n=30) or Thyrogen (n=33)
- Scintigraphic neck images were acquired starting 48 hrs after RAI administration to assess biokinetics in the thyroid remnant.
- Activity in blood samples was quantified and data from whole-body probe measurements and scintigraphic whole-body scans were combined to deduce retention curves in blood and whole body, respectively.
- The absorbed dose to the blood was calculated.1
Thyrogen (rhTSH) increases TSH levels rapidly after administration allowing patients to remain on thyroid hormone.
.jpg 400w, /.imaging/webp/sanofi-platform/img-w500/dam/Thyrogen-hcp/clinical-pharmacology/chartstudyoverview--1-.jpg/jcr:content/chartstudyoverview%20(1).jpg 500w)
Reduced numbers of patients with whole-body and blood dose data are due to technical failures during whole-body measurements.

Serum TSH Concentration1
The pharmacokinetics of rhTSH were studied in 16 patients with well differentiated thyroid cancer given a single intramuscular dose of 0.9 mg. Mean peak serum TSH concentrations of 116 ± 38 mU/L were reached between 3 and 24 hours after injection (median of 10 hours). The mean apparent elimination half-life was 25 ± 10 hours. The organ(s) of TSH clearance in humans have not been identified, but studies of pituitary-derived TSH suggest involvement of the liver and kidneys.2
The Use of Thyrogen During Remnant Ablation
Watch how patients can start on a thyroid hormone immediately after surgery, and remain euthyroid during remnant ablation with Thyrogen.
Choose how to get Thyrogen (thyrotropin alfa) for your patients
Not sure which one to choose? Contact ThyrogenONE for assistance

Option 1: Sign up or log into the ThyrogenONE portal
The ThyrogenONE portal provides your office online access to help you and your patients :
- Submit and track benefit verifications
- Coordinate orders
- Generate automatic alerts

Option 2: Call ThyrogenONE at 1-88-THYROGEN (1-888-497-6436) (
Dedicated ThyrogenONE Case Managers can assist you and your patients with the following.
- Benefits Verification
- Information on Ordering
- Information on specialty pharmacy fulfillment
Important Safety Information and Indications
Important Safety Information and Indications
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
If Thyrogen is administered with radioiodine, the contraindications to radioiodine also apply to this combination regimen. Refer to the radioiodine prescribing information for a list of contraindications for radioiodine.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Thyrogen-Induced Hyperthyroidism:
- There have been reports of death in non-thyroidectomized patients and in patients with distant metastatic thyroid cancer in which events leading to death occurred within 24 hours after administration of Thyrogen. Caution should be exercised in patients who have substantial thyroid tissue still in situ or functional thyroid cancer metastases, specifically in the elderly and those with a known history of heart disease.
- Hospitalization for administration of Thyrogen and post-administration observation in patients at risk should be considered.
Stroke:
- There are post marketing reports of stroke in young women with risk factors for stroke, and neurological findings suggestive of stroke (e.g., unilateral weakness) occurring within 72 hours of Thyrogen administration in patients without known central nervous system metastases. The relationship between Thyrogen administration and stroke is unknown. Patients should be well-hydrated prior to treatment with Thyrogen.
Sudden Rapid Tumor Enlargement:
- Sudden, rapid and painful enlargement of residual thyroid tissue or distant metastases can occur following treatment with Thyrogen. Pretreatment with glucocorticoids should be considered for patients in whom tumor expansion may compromise vital anatomic structures.
Risks Associated with Radioiodine Treatment:
- If Thyrogen is administered with radioiodine (RAI), the warnings and precautions for RAI apply to this combination regimen. Refer to the RAI prescribing information for a full list of the warnings and precautions for RAI.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials were nausea and headache.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy:
- If Thyrogen is administered with radioiodine, the combination regimen is contraindicated in pregnant women.
- Available data with Thyrogen use in pregnant women are insufficient to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Lactation:
- The concomitant use of Thyrogen and radioiodine (RAI) is contraindicated in lactating women. If Thyrogen is administered with RAI for diagnostic use, discontinue breastfeeding after RAI administration because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from RAI in the breastfed infant.
- If Thyrogen is not administered with RAI, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Thyrogen and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child. There are no available data on the presence of thyrotropin alfa in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use: Results from controlled trials do not indicate a difference in the safety and efficacy of Thyrogen between adult patients less than 65 years and those over 65 years of age.
Renal Impairment: Elimination of Thyrogen is significantly slower in dialysis-dependent end stage renal disease patients, resulting in prolonged elevation of TSH levels.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Thyrogen® (thyrotropin alfa) is a thyroid stimulating hormone indicated for:
Adjunctive Diagnostic Tool for Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Use as an adjunctive diagnostic tool for serum thyroglobulin (Tg) testing with or without radioiodine imaging in the follow-up of patients with well-differentiated thyroid cancer who have previously undergone thyroidectomy.
Limitations of Use:
- Thyrogen-stimulated Tg levels are generally lower than, and do not correlate with Tg levels after thyroid hormone withdrawal.
- Even when Thyrogen-Tg testing is performed in combination with radioiodine imaging, there remains a risk of missing a diagnosis of thyroid cancer or underestimating the extent of the disease.
- Anti-Tg Antibodies may confound the Tg assay and render Tg levels uninterpretable.
Adjunct for Thyroid Remnant Ablation in Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Use as an adjunctive treatment for radioiodine ablation of thyroid tissue remnants in patients who have undergone a near-total or total thyroidectomy for well-differentiated thyroid cancer and who do not have evidence of distant metastatic thyroid cancer.
Limitations of Use:
- The effect of Thyrogen on thyroid cancer recurrence greater than 5 years post-remnant ablation has not been evaluated.
Click here for full Prescribing Information
Important Safety Information and Indications
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
If Thyrogen is administered with radioiodine, the contraindications to radioiodine also apply to this combination regimen. Refer to the radioiodine prescribing information for a list of contraindications for radioiodine.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Thyrogen-Induced Hyperthyroidism:
- There have been reports of death in non-thyroidectomized patients and in patients with distant metastatic thyroid cancer in which events leading to death occurred within 24 hours after administration of Thyrogen. Caution should be exercised in patients who have substantial thyroid tissue still in situ or functional thyroid cancer metastases, specifically in the elderly and those with a known history of heart disease.
- Hospitalization for administration of Thyrogen and post-administration observation in patients at risk should be considered.
Stroke:
- There are post marketing reports of stroke in young women with risk factors for stroke, and neurological findings suggestive of stroke (e.g., unilateral weakness) occurring within 72 hours of Thyrogen administration in patients without known central nervous system metastases. The relationship between Thyrogen administration and stroke is unknown. Patients should be well-hydrated prior to treatment with Thyrogen.
Sudden Rapid Tumor Enlargement:
- Sudden, rapid and painful enlargement of residual thyroid tissue or distant metastases can occur following treatment with Thyrogen. Pretreatment with glucocorticoids should be considered for patients in whom tumor expansion may compromise vital anatomic structures.
Risks Associated with Radioiodine Treatment:
- If Thyrogen is administered with radioiodine (RAI), the warnings and precautions for RAI apply to this combination regimen. Refer to the RAI prescribing information for a full list of the warnings and precautions for RAI.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials were nausea and headache.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy:
- If Thyrogen is administered with radioiodine, the combination regimen is contraindicated in pregnant women.
- Available data with Thyrogen use in pregnant women are insufficient to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Lactation:
- The concomitant use of Thyrogen and radioiodine (RAI) is contraindicated in lactating women. If Thyrogen is administered with RAI for diagnostic use, discontinue breastfeeding after RAI administration because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from RAI in the breastfed infant.
- If Thyrogen is not administered with RAI, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Thyrogen and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child. There are no available data on the presence of thyrotropin alfa in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use: Results from controlled trials do not indicate a difference in the safety and efficacy of Thyrogen between adult patients less than 65 years and those over 65 years of age.
Renal Impairment: Elimination of Thyrogen is significantly slower in dialysis-dependent end stage renal disease patients, resulting in prolonged elevation of TSH levels.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Thyrogen® (thyrotropin alfa) is a thyroid stimulating hormone indicated for:
Adjunctive Diagnostic Tool for Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Use as an adjunctive diagnostic tool for serum thyroglobulin (Tg) testing with or without radioiodine imaging in the follow-up of patients with well-differentiated thyroid cancer who have previously undergone thyroidectomy.
Limitations of Use:
- Thyrogen-stimulated Tg levels are generally lower than, and do not correlate with Tg levels after thyroid hormone withdrawal.
- Even when Thyrogen-Tg testing is performed in combination with radioiodine imaging, there remains a risk of missing a diagnosis of thyroid cancer or underestimating the extent of the disease.
- Anti-Tg Antibodies may confound the Tg assay and render Tg levels uninterpretable.
Adjunct for Thyroid Remnant Ablation in Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Use as an adjunctive treatment for radioiodine ablation of thyroid tissue remnants in patients who have undergone a near-total or total thyroidectomy for well-differentiated thyroid cancer and who do not have evidence of distant metastatic thyroid cancer.
Limitations of Use:
- The effect of Thyrogen on thyroid cancer recurrence greater than 5 years post-remnant ablation has not been evaluated.
Click here for full Prescribing Information
References
1) Data on file. Thyrogen Value Dossier. April 22, 2013, Sanofi Genzyme.
2) Hanscheid H, et al. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:648-654

.png)

.jpg 400w, /.imaging/webp/sanofi-platform/img-w500/dam/Thyrogen-hcp/clinical-pharmacology/pagebanner--4-.jpg/jcr:content/pagebanner%20(4).jpg 500w)